VisTools
This section describes the calculations in the Visualyse Interplanetary stand-alone tool kit, VisTools.
- dB Calculation
- Frequency to Wavelength
- Path Loss
- Field of View
- Peak Gain
- Half Power Beamwidth
- Relative Gain
- Temperature to Noise
- Link Budget
dB Calculation
The tool converts between (d) and absolute (a) using:
Frequency to Wavelength
The Frequency tool converts between frequency and wavelength using:
where is the speed of light
Path Loss
The Pathloss tool calculates the free space path loss. The parameters used are:
- Frequency and Frequency units
- Path Length
- Path Loss
Each of these three can be calculated from the other using:
Field of View
The field of view tool provides information about circular orbits in terms of field of view and orbit period. The parameters are:
- height of satellite
- distance to horizon
- half of field of view,
- orbital period
as shown in the figure below:
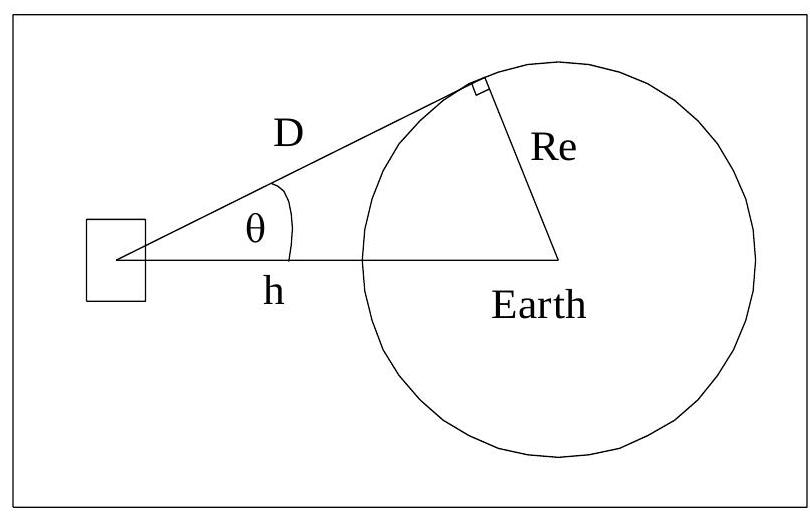
The equations are:
where:
Peak Gain
This tool calculates peak gain based on the following parameters:
- frequency and frequency units
- dish size D
- efficiency
- peak gain
These parameters are related using the following equation:
Half Power Beamwidth
The Theta-3dB tool calculates half power beamwidth based upon the following parameters:
- peak gain,
- efficiency,
- half power beamwidth,
These parameters are related using the following equation:
Relative Gain
The relative gain tool calculates offaxis gain within the main lobe for a pure parabolic dish, based upon the following parameters:
- Gain relative to peak,
- Half power beamwidth,
- Offaxis angle, These parameters are related using the following equation:
Temperature to Noise
The noise tool converts between temperature in Kelvin to noise in . The following parameters are used:
- Temperature in Kelvin
- Noise in
These parameters are related using the following equations:
where is Boltzmann's constant in .
Link Budget
These various tools are combined to produce a link budget tool with the following parameters:
- Frequency, f, entered either directly or using the frequency tool
- Transmit power, P, entered directly, or calculated from transmit EIRP
- Transmit peak gain , entered either directly or using the peak gain tool
- Transmit relative gain , entered either directly or using the offaxis gain tool
- Transmit eirp, EIRP, either entered directly or calculated from or using:
- Free space path loss, , either entered directly or using the pathloss tool
- Other losses, , entered directly
- Receive peak gain , entered either directly or using the peak gain tool
- Receive relative gain , entered either directly or using the offaxis gain tool
- Receive power, C, either entered directly or calculated from EIRP or or using
- Receive noise, , either entered directly or using the noise tool
- Receive , either entered directly or calculated using:
Note that: - If is changed directly the , EIRP and transmit power fields update accordingly
- If the EIRP field is changed directly, the , and transmit power fields update accordingly
- If the transmit power field is changed directly, the EIRP, and , fields update accordingly
- If the field is changed directly the C, EIRP, and transmit fields update accordingly