Example Files
This document describes the example files supplied with the Version 7 of Visualyse Interplanetary. They have been selected to give an idea how Visualyse Interplanetary can model a range of radio systems and sharing scenarios.
Visualyse Interplanetary is a very flexible tool to study interference between radio systems, in particular radio communication systems. We have grouped the example files into the following categories:
- Aeronautical
- Digital Dividend
- Earth station coordination
- Fixed planning and coordination
- GSO to GSO Satellite
- Maritime
- Military
- Network Coverage
- Non-GSO Satellites
- Others
- PCS/AWS
- Radiolocation
- Satellite & Terrestrial
- Short range devices
- Space Science Service
Some files require one or more of the Modules that enhance the main product:
At the start of each section there is a table which shows the modules needed for that example file. In the case of the Terrain Module it is also necessary to have the right terrain data file available, so these are also listed. The terrain files should be in the Visualyse 7/Terrain directory.
If you have a full version of Visualyse Interplanetary you can also look at these files: however, should the example file use a Module for which you do not have a license, the demonstration might work incorrectly. In this case remove your dongle so that you operate in Demonstration Mode.
Hint: You can change the parameters to see how that would impact the results, but only at the start. You might have to reset the simulation to start: “Rewind” button on the control bar.
Note: These simulation files have in places been simplified for clarity.
Visualyse Interplanetary
Visualyse Interplanetary is the most widely used study tool within the ITU-R for interference analysis and radio compatibility with over 200 papers produced using it.
Visualyse Interplanetary helps you model complex radio communication systems, including terrestrial, aeronautical, maritime and satellite, including:
- Sophisticated antenna modelling, including single beam, multiple beam, symmetric beams (as in the figure below), and fixed, random, tracking, rotating pointing methods

- Detailed gain pattern modelling – e.g. ITU-R Recs, shaped and GIMS contour beams, as in the figures below:
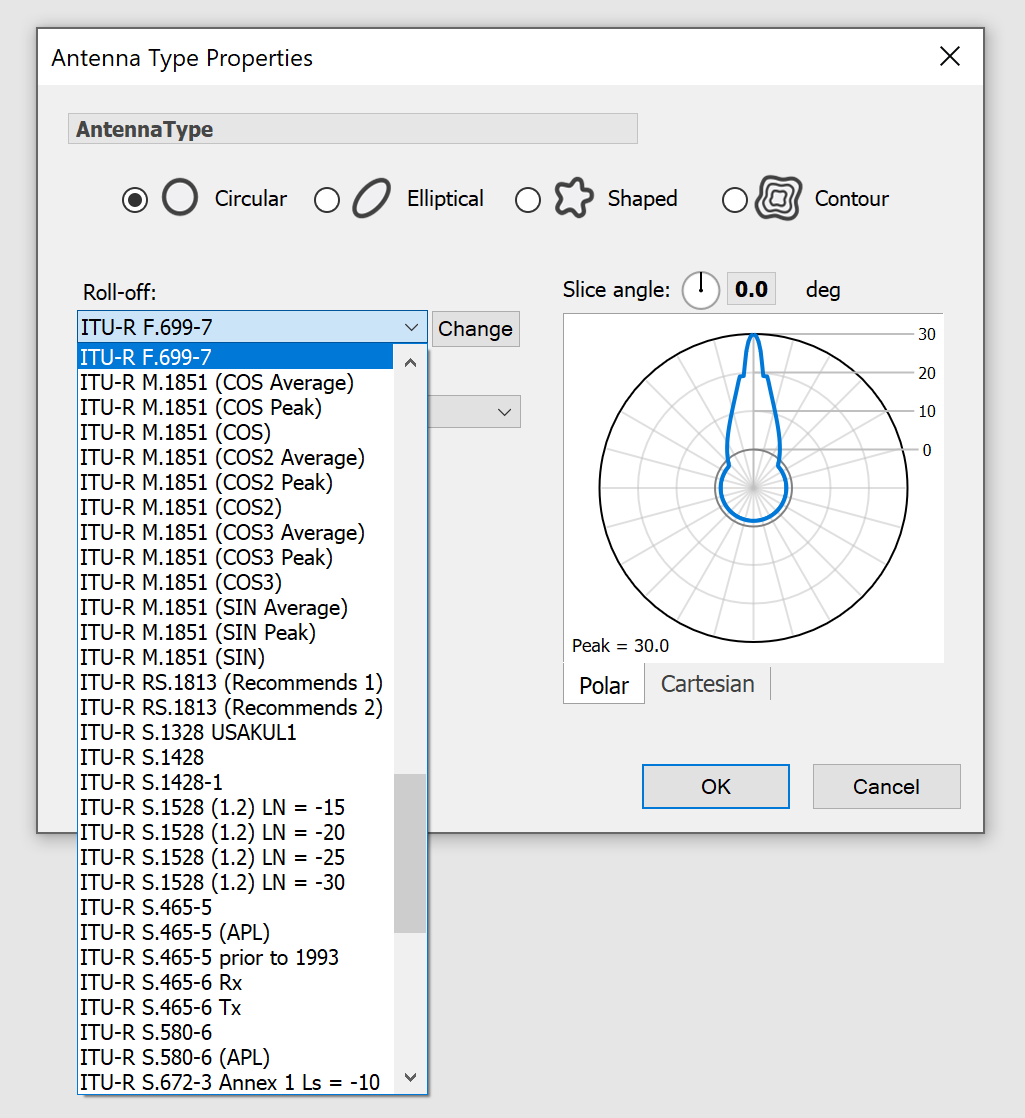
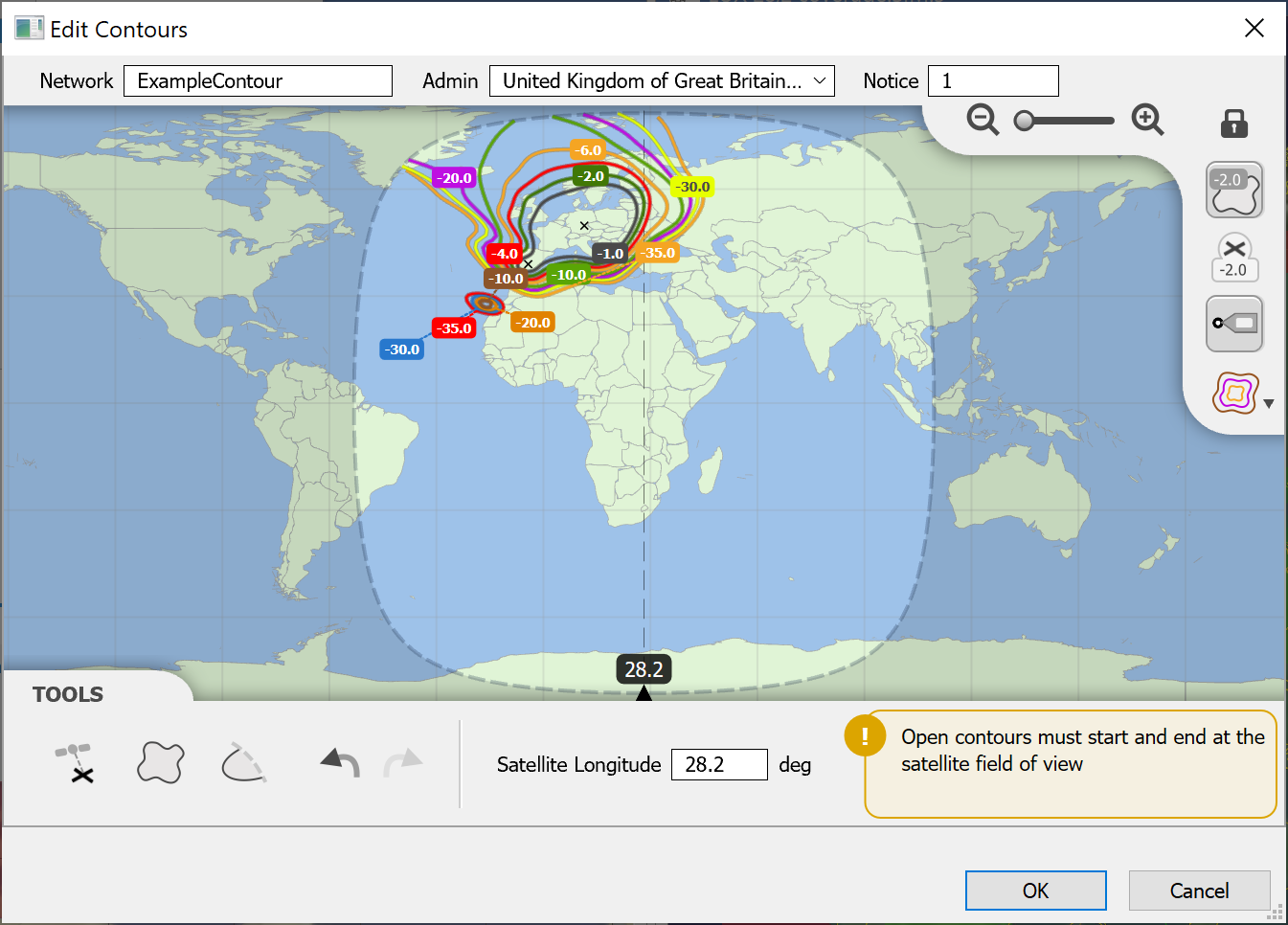
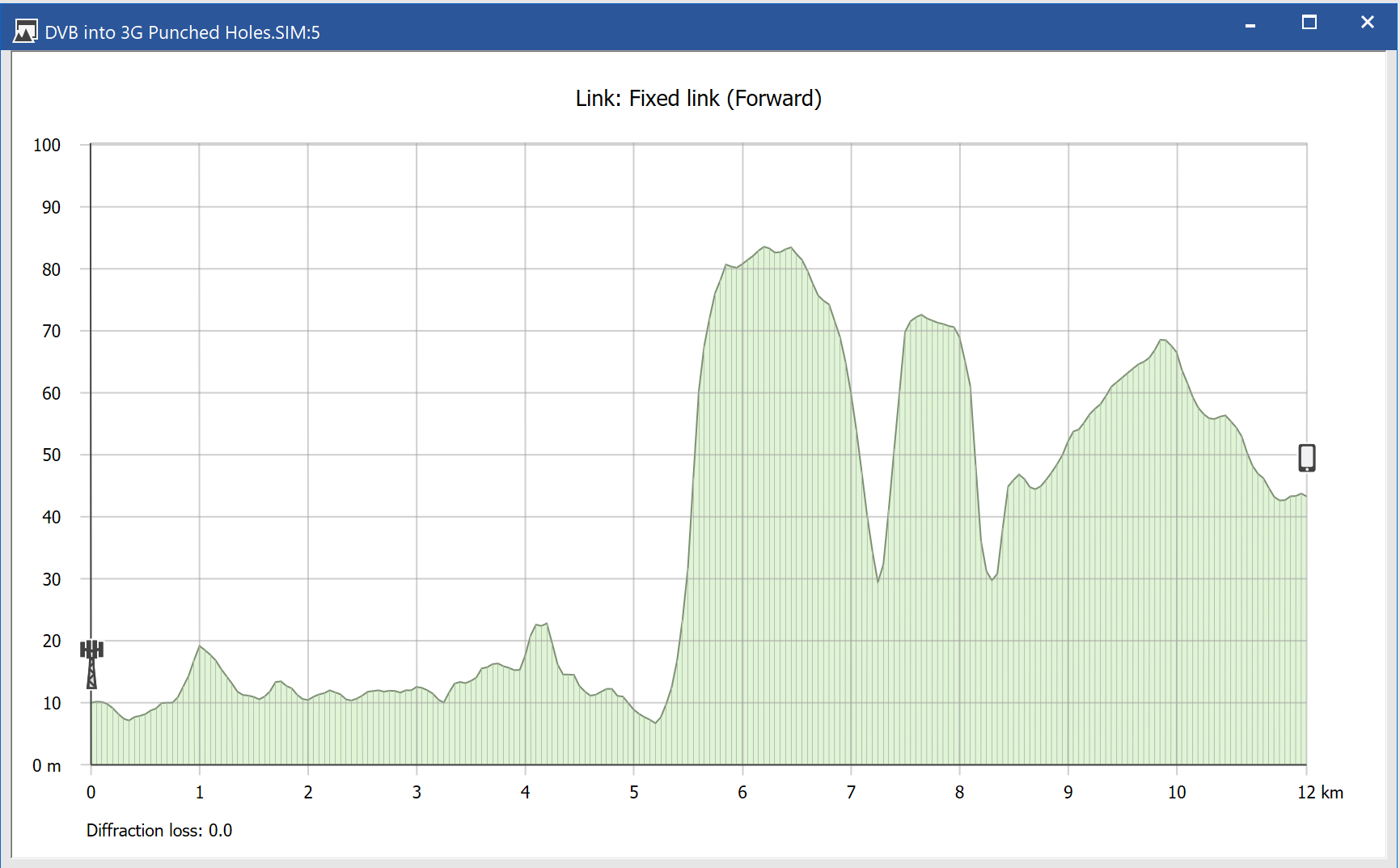
- Library of propagation models including terrestrial mobile, fixed & broadcasting, and earth to/from space, including those in the figure below.

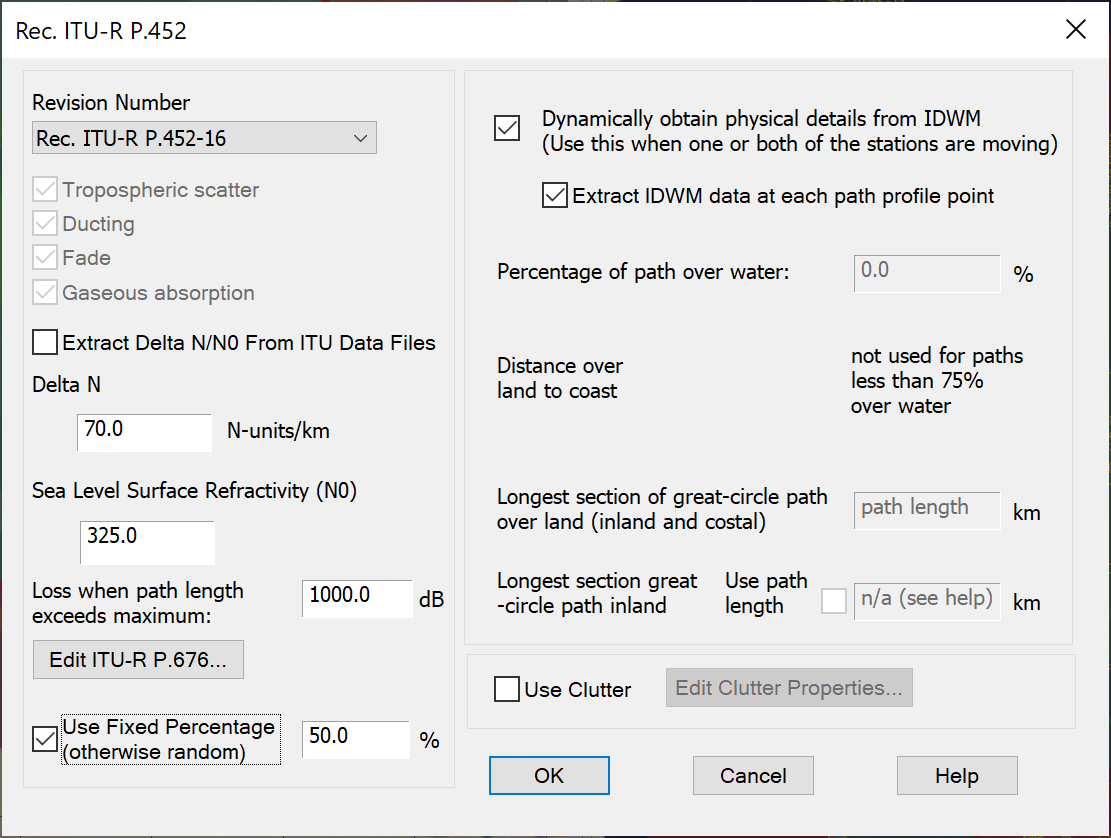
- Dynamics of mobile stations, ships, aircraft and satellites (GSO, HEO, and non-GSO)
- Access to intermediate calculations including link budgets, terrain path profiles, and geometry
- Link performance criteria including C, I, C/I, I/N, C/(N+I), PFD, EPFD, FDP, plus statistics where required
- Data import tools for station locations, fixed links, SRS for GSO and non-GSO satellites, and terrestrial IFIC data
- Monte Carlo any variable or use a sequence of pre-defined values
- Interface to terrain and land-use databases, and use within propagation models
- Ability to see impact of varying the location of a station of almost any of the results (i.e. to plot coverage, elevation angles, interference etc.)